Lipid Photooxidation Products Induce Melanoma Cell Death
Melanoma is the most aggressive type of skin cancer. Although less common, it is the most serious, due to its metastatic potential. Despite the health benefits of sunlight, prolonged exposure to the sun remains the principal risk factor for developing the disease. Excessive radiation triggers oxidative stress and inflammation in skin cells via photooxidation.
Both ultraviolet and visible light can activate photosensitizers naturally present in tissues. This process converts light energy into chemical energy, generating reactive oxygen species that damage biomolecules, such as the lipids in cell membranes. However, these reactions can also be harnessed for therapeutic purposes, such as photodynamic therapy, which targets tumor cells or pathogens.
Now, researchers from the RIDC Redoxoma, led by Professor Sayuri Miyamoto from the Instituto de Química at Universidade de São Paulo (USP), have discovered that endoperoxides derived from the oxidation of ergosterol and 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC)—both sterol-class lipids—induce melanoma cell death. These endoperoxides, in combination with photodynamic therapy, may open up possibilities for developing innovative formulations, including nanoparticles, as potential alternatives for melanoma treatment.
“The major challenge with melanoma is its rapid progression. Although not the first-line treatment, photodynamic therapy is gaining significant attention because it is less invasive than conventional methods, such as surgery. Our focus in this work was to optimize photodynamic therapy, and to achieve that, we needed to understand what happens in cell membranes,” said Megumi Nishitani Yukuyama, lead author of the article published in the journal Photochemistry and Photobiology.
This finding is part of a broader study to understand the mechanisms behind light-induced oxidative damage in cell membranes. The researchers analyzed and compared how the photooxidation of types I and II of ergosterol, 7-DHC, and cholesterol affects cell membranes. They also identified and characterized the main products formed during these oxidation processes.
“This study is important to understand the oxidation mechanism of these sterols in membranes when exposed to different oxidants. It also helps us determine which oxidation products are formed and their effects on membrane integrity,” said Miyamoto.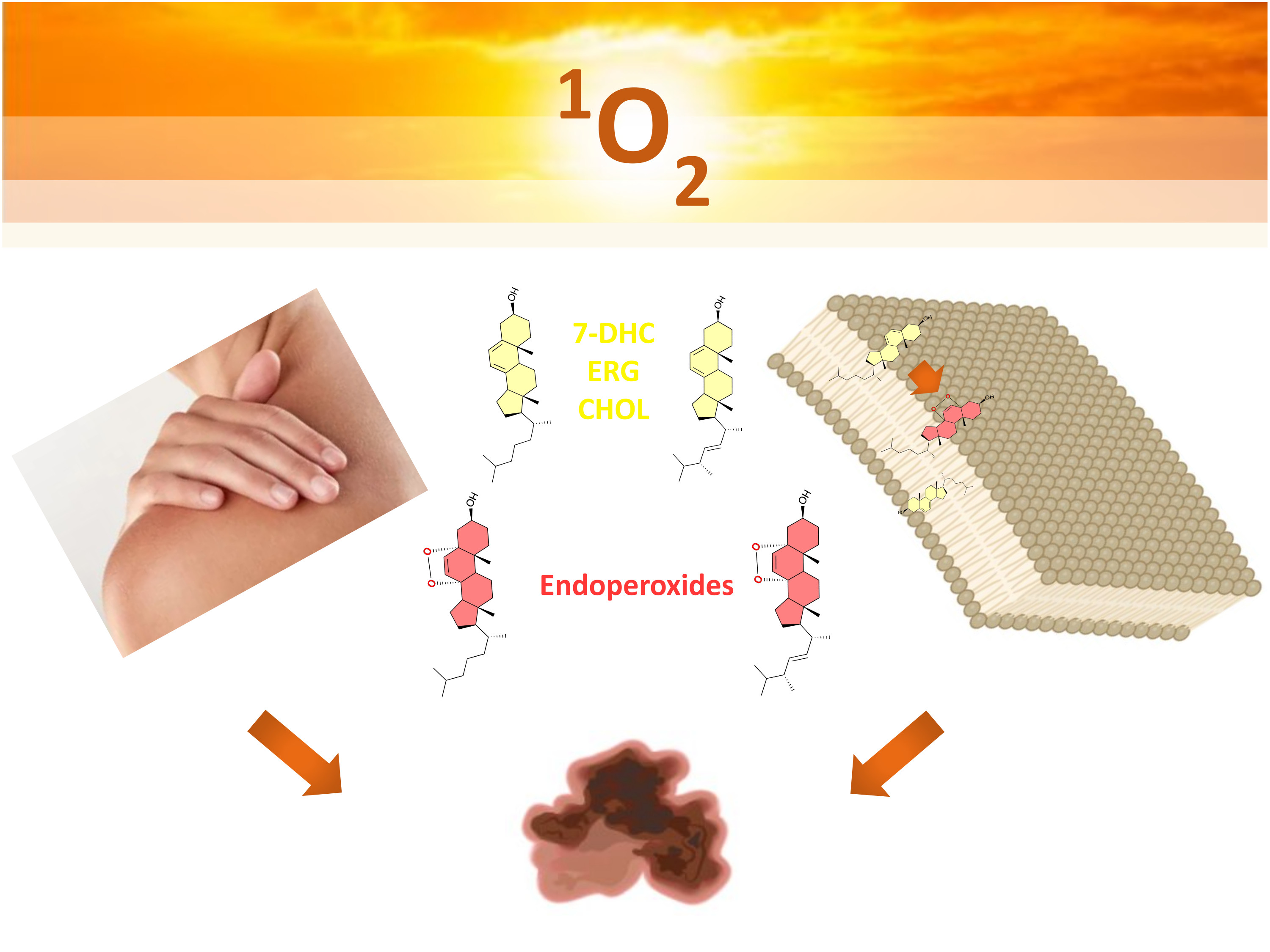
Sterols and photooxidation
A new finding of the research was that the cell membrane permeability changes depending on the type of oxidative damage. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane composed of a lipid bilayer associated with proteins. The structural basis of the bilayer is formed by phospholipids, which are susceptible to oxidations. Such oxidative damage can compromise membrane integrity, increasing permeability and potentially leading to cell death.
Photooxidation reactions are classified into two main mechanisms. In type I reaction, reactive radical species are formed, such as the superoxide radical anion and hydroperoxyl radicals. In a type II reaction, singlet molecular oxygen, a highly reactive form of oxygen, is produced.
The study revealed that, in radical-mediated oxidations (type I), the sterols ergosterol and 7-DHC provide greater membrane protection than cholesterol. However, in oxidations mediated by singlet oxygen (type II), cholesterol proved more effective.
This suggests that in type II oxidations, cholesterol functions as an antioxidant. “It organizes the membrane in such a way that singlet oxygen cannot access the unsaturated lipids that would otherwise be oxidized. This assay demonstrated that cholesterol is crucial for protecting cell membranes against light-induced damage,” Miyamoto explained.
However, when protecting the membranes, these sterols undergo oxidation, generating several products, including endoperoxides. The study showed that endoperoxides derived from 7-DHC and ergosterol are the most stable in these processes. “In the work we published last year in Nature, we showed that 7-DHC functions as an antioxidant, protecting cells against death by ferroptosis in radical-mediated oxidation reactions. However, when performing this function, it is oxidized and generates several products,” said Miyamoto.
7-DHC is a precursor of cholesterol, and both are common sterols in mammals. Ergosterol is a sterol found in yeast with a structure similar to 7-DHC. Upon oxidation, it also generates endoperoxides. According to Yukuyama, “The literature on ergosterol was somewhat controversial. That’s why we conducted a comparative study to clarify the mechanisms behind the protective or harmful effects of these sterols.“
They also assessed the viability of melanoma cell A375 treated with 7-DHC, ergosterol, and their endoperoxides generated through photodynamic therapy, a process that induces type I and type II oxidation. Notably, the endoperoxides of ergosterol and 7-DHC produced by singlet oxygen were more effective at killing melanoma cells than their precursor molecules.
“Next, we aim to investigate how different concentrations of endoperoxides and varying radiation doses influence their effects. The study has opened the door to many new questions,” concluded Yukuyama.
In addition to the team from the Laboratory of Modified Lipids and Redox Biochemistry of the Instituto de Química at USP, the work was conducted in collaboration with the researcher groups of Professors Maurício Baptista and Paolo Di Mascio, both from the IQ-USP and members of the RIDC Redoxoma, and Miriam Uemi, from the Universidade Federal de São Paulo. This article is part of a Special Issue commemorating the XV ELAFOT/ 1st LatASP Conference held from October 23rd to 26th, 2023 in Maresias Beach, Brazil.
The article Comparative study of ergosterol and 7-dehydrocholesterol and their endoperoxides: Generation, identification, and impact in phospholipid membranes and melanoma cells, by Megumi Nishitani Yukuyama, Karen Campos Fabiano, Alex Inague, Miriam Uemi, Rodrigo Santiago Lima, Larissa Regina Diniz, Tiago Eugenio Oliveira, Thais Satie Iijima, Hector Oreliana Fernandes Faria, Rosangela Silva Santos, Maria Fernanda Valente Nolf, Adriano Brito Chaves-Filho, Marcos Yukio Yoshinaga, Helena Couto Junqueira, Paolo Di Mascio, Mauricio da Silva Baptista, and Sayuri Miyamoto, is available here.
